Cipher Mining announced a $2 billion offer from its subsidiary Black Pearl Compute LLC to build a large data center in Texas.
The funds will be used to build Cipher Mining's Black Pearl facility. The facility has a total power capacity of 300 megawatts (MW).
Why is the focus of crypto mining shifting from Bitcoin to high-performance computing?
Cipher Mining Co., Ltd. announced The company's wholly-owned subsidiary, Black Pearl Computing LLC, announced that it plans to issue $2 billion in senior secured notes to fund its AI ambitions. The bonds have an issuance deadline of 2031 and will be sold in a private placement to large institutional investors.
Cipher started as a Bitcoin miner, but has now rebranded as a leader in industrial-scale data centers for high performance computing (HPC). The $2 billion will be used to pay for the remaining construction costs at the Black Pearl facility in Wink, Texas.
It will also be used to reimburse the approximately $232.5 million that Cipher Mining spent on the project. The rest will be used for public debt service reserves and various fees.
The Black Pearl facility is an important part of Cipher's future. The site is 70 acres with a total power generation capacity of 300 megawatts (MW). Phase I of the project, delivering 150 MW, was commissioned in 2025.
Cipher's decision to expand into HPC infrastructure comes as Bitcoin mining becomes less profitable. In early 2026, the global Bitcoin hashrate reached an all-time high, making it harder and more expensive for miners to earn rewards.
Additionally, Bitcoin's “hash price,” which measures the daily revenue miners earn per unit of power, continued to decline throughout the first quarter of 2026.
The halving event in 2024, which cut Bitcoin rewards in half, created a “tight margin environment” and many public mining companies realized that relying solely on Bitcoin in 2025 and 2026 was too risky.
Building data centers for HPC allows Cipher Mining to enter into long-term lease agreements with major technology companies such as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft.
In late 2025, the company signed a large 15-year lease with Amazon Web Services (AWS) for 300 MW of capacity. The deal is estimated to generate $5.5 billion in revenue over the period. Cipher also has a $3 billion hosting deal with Google-backed Fluidstack.
Companies like TeraWulf and Core Scientific are also pivoting to AI infrastructure. TeraWulf recently expanded its Texas facility to manage AI workloads, and Core Scientific signed a multibillion-dollar contract with CoreWeave.
These companies are now viewed by investors as traditional data center operators and often trade at higher valuations because their revenues are more predictable.
What is the financial risk of a $2 billion bond issue?
The “issuer” of the debt is Black Pearl Compute LLC. The debt is “priority secured,” meaning the lender has first priority claim against the asset if things go south.
The bonds are guaranteed by two other subsidiaries that own actual land and equipment in Texas: Cipher Black Pearl LLC and 11786 Wink LLC. This debt is secured by liens on substantially all of the assets of these entities. Essentially, the Black Pearl Facility itself serves as collateral for the $2 billion loan.
Parent company Cipher Mining also promised lenders that if $2 billion is not enough to complete the Texas facility, it will provide the additional funds needed to complete the work on time.
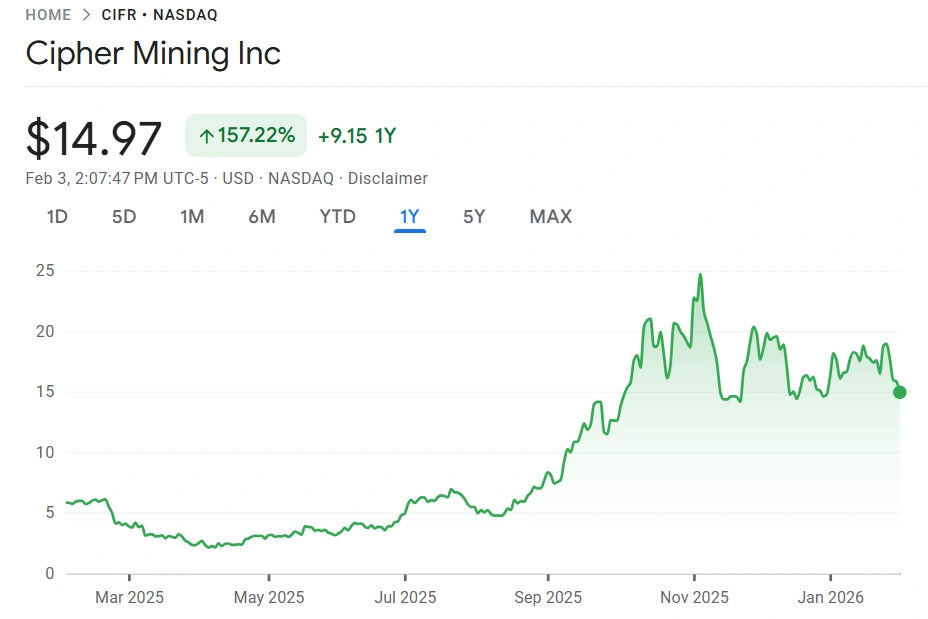
crypto stock. Source: Google Finance
As of February 2026, Cipher's stock has returned 156% over the past year, despite its high debt and recent stock price decline. Although the latest quarterly report from late 2025 shows a net loss, management emphasized that “adjusted earnings” remain positive as the Bitcoin mining business is still generating cash.
The Notes are offered under Regulation 144A and Regulation S and are therefore available only to Qualified Institutional Purchasers and certain persons outside the United States.

